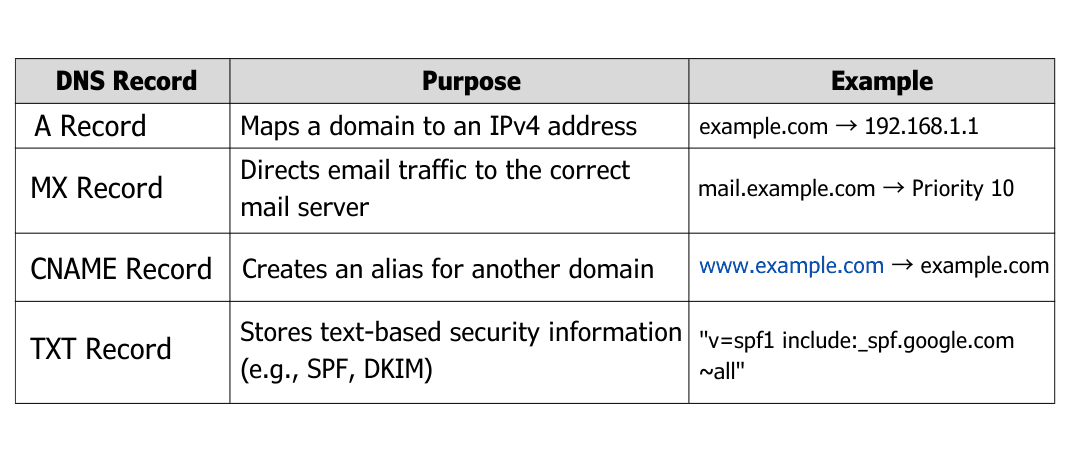
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the backbone of the internet, translating human-friendly domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. Without DNS, websites would be nearly impossible to navigate, and businesses would struggle to maintain an online presence.
However, DNS records are not just about connectivity—they play a crucial role in cybersecurity, email communication, and brand integrity. Failing to monitor DNS records can expose your business to cyber threats, downtime, and data breaches.
In this article, we will explore the importance of DNS records, the risks of neglecting DNS monitoring, and how businesses can protect their domains from cyber threats. We will also look at real-world DNS attacks, best practices for DNS security, and essential tools for proactive DNS monitoring.
For a broader understanding of domain management, check out our article on Domain Expiration: How Monitoring Can Save Your Business from Downtime.